The shoulder is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the human body, making it susceptible to various injuries. Shoulder injuries can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and recovery. This blog delves into the common types of shoulder injuries, their causes, symptoms, and the available treatment options.
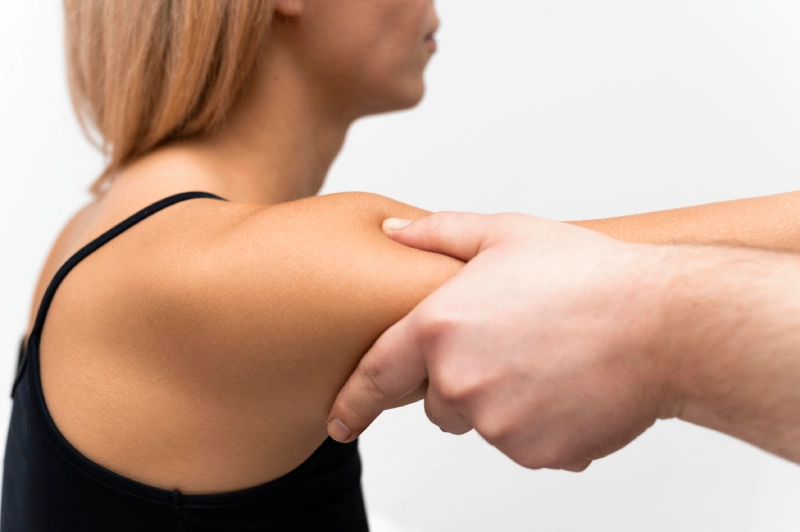
Common Types of Shoulder Injuries
- Rotator Cuff Tears
- Dislocations
- Fractures
- Impingement Syndrome
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
- Labral Tears
- Arthritis
Causes of Shoulder Injuries
Shoulder injuries can result from various factors, including:
- Trauma: Direct blows to the shoulder from accidents, falls, or sports injuries.
- Overuse: Repetitive motions, especially in sports like baseball, tennis, and swimming, or jobs requiring overhead activities.
- Aging: Degenerative changes in the shoulder structures, such as tendons and cartilage, making them more prone to injury.
- Poor Posture: Chronic poor posture can lead to shoulder impingement and other issues.
- Weakness and Imbalance: Muscle weakness or imbalance can increase the risk of shoulder injuries.
Symptoms of Shoulder Injuries
The symptoms of shoulder injuries can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Sharp or dull pain in the shoulder, which may worsen with movement.
- Swelling and Bruising: Around the shoulder and sometimes extending down the arm.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty moving the shoulder or arm, often accompanied by stiffness.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in the shoulder and arm.
- Deformity: Visible deformity in cases of dislocation or severe fractures.
- Clicking or Popping: Sensations of clicking, popping, or catching inside the shoulder.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Injuries
To diagnose a shoulder injury, an orthopedic doctor will typically:
- Conduct a Physical Examination: Assess the shoulder for signs of deformity, swelling, tenderness, and range of motion.
- Order Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Injuries
Treatment for shoulder injuries depends on the type and severity of the injury, as well as the patient’s overall health and activity level.
- Non-Surgical Treatment
- Rest and Immobilization: Using a sling or shoulder immobilizer to keep the shoulder in place and allow it to heal.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) to manage pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to restore movement and strength, and reduce pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: To reduce inflammation and pain in certain conditions like rotator cuff tears or impingement syndrome.
- Surgical Treatment
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to repair torn tendons, ligaments, or cartilage.
- Open Surgery: For more severe injuries, such as complex fractures or significant rotator cuff tears, open surgery may be necessary.
- Joint Replacement: In cases of severe arthritis or irreparable damage, partial or total shoulder replacement may be recommended.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from shoulder injuries can take several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method used. Key aspects of recovery include:
- Rest: Adequate rest and avoiding activities that stress the shoulder.
- Physical Therapy: Gradual rehabilitation exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider to monitor healing progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Prevention of Shoulder Injuries
While not all shoulder injuries can be prevented, some measures can reduce the risk:
- Strengthening Exercises: Regular exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles and maintain balance.
- Proper Technique: Using correct techniques in sports and daily activities to avoid strain.
- Ergonomics: Ensuring proper ergonomics at work and during physical activities.
- Stretching: Regular stretching to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Protective Gear: Using appropriate protective equipment when engaging in sports or activities with a high risk of shoulder injury.
Conclusion
Shoulder injuries are common and can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate medical care are essential steps in managing shoulder injuries. With the right treatment and rehabilitation, most people can regain full function of their shoulders and return to their normal activities.